Coronary Artery Disease
Coronary artery disease is a disease in which a fatty substance called plaque builds up inside the coronary arteries. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle. When plaque builds up in these arteries, it limits the blood flow supply to your heart, resulting in less oxygen delivery and heart muscle dysfunction. This can cause chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, or other symptoms that can be warning signs of significant blockage. These signs can indicate an impending heart attack. Interventional cardiology is the aspect of cardiology that helps diagnose and treat these blockages.
Angiogram / Heart Catheterization
What is it?
An angiogram, also known as a heart catheterization, is a specialized test done under X-ray, that shows the blood flow through the coronary arteries. The coronary arteries are responsible for supplying oxygenated blood to your heart. During the procedure, your doctor makes a small incision in the wrist (radial artery) or groin (femoral artery) and advances a long thin tube, called a catheter, through the artery leading up into your coronary artery in the heart. Your doctor then injects a special fluid called contrast media, or contrast dye, through the catheter into your heart’s blood stream.
The contrast dye allows the x-ray to show real time moving images of the blood flow through the coronary arteries. The doctor uses these images to identify the precise location of any blockages in your arteries and the extent of plaque buildup. Based on the findings of this test, your doctor is able to determine if further treatment such as coronary angioplasty, coronary, stents, or open heart surgery is needed to fix the lack of blood supply.
Video explaining angiogram / heart catheterization, coronary angioplasty (PCI), and coronary stent:
Coronary Angioplasty / Percutaneous Intervention (PCI)
What is it?
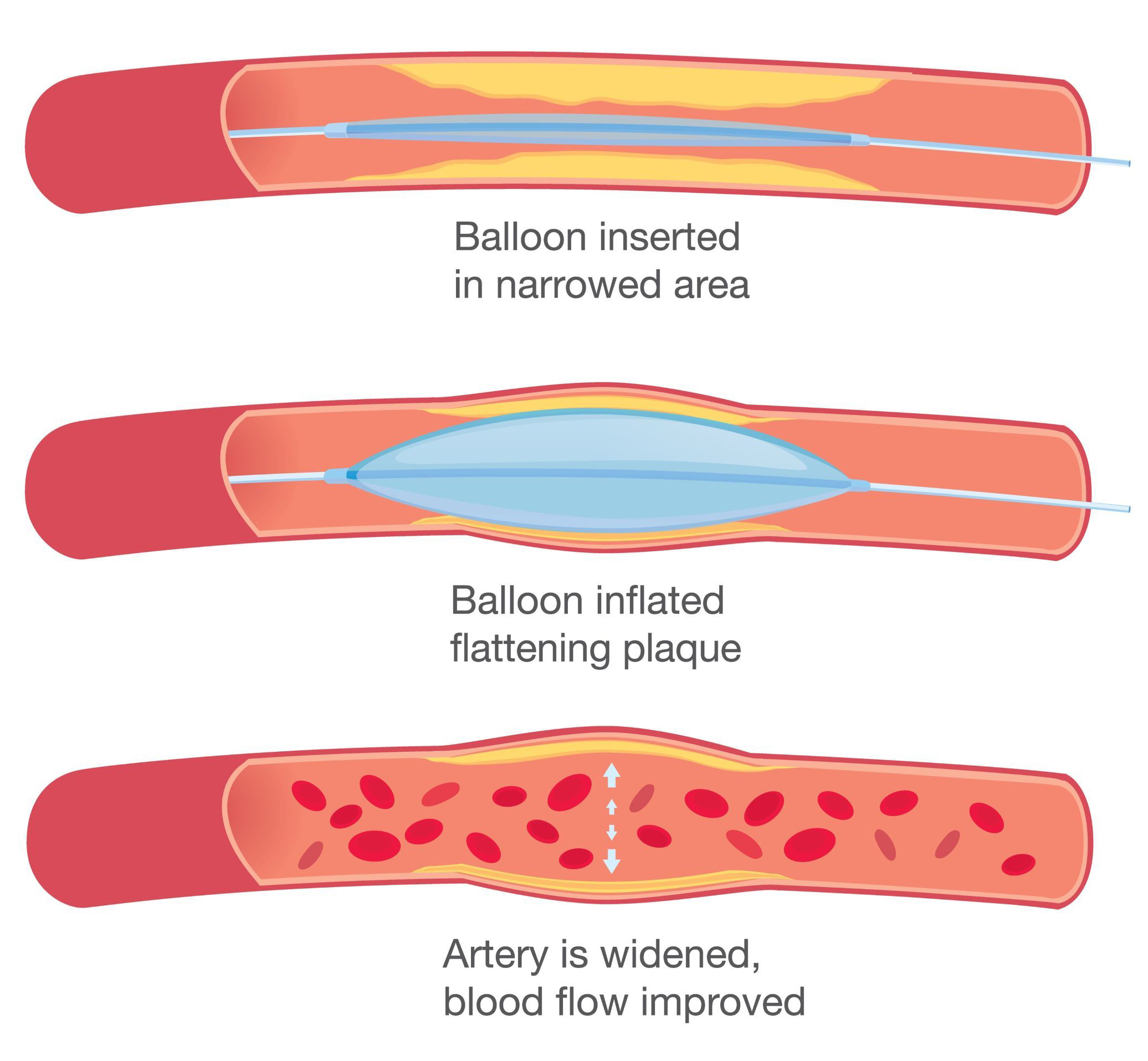
A coronary angioplasty, also known as Percutaneous Intervention (PCI), is a minimally invasive procedure that can improve blood flow to the heart when a person has coronary artery disease. Our doctor advances a catheter (a long narrow tube) with a tiny balloon on its tip up into the artery until it reaches the site that the plaque buildup is causing the blockage. A wire is then passed through the blocked area that allows the doctor to use the equipment necessary to fix the blockage.
The equipment can include balloons, stents or other more specialized devices depending on the nature and severity of the disease. These devices are then passed along the wire to the desired location. The balloon is inflated to compress the plaque against the artery wall, opening up the passageway and restoring blood flow. The balloon is then deflated and removed. In most cases, your doctor may determine that a coronary stent needs to be inserted where the blockage was to keep the artery open after the balloon is removed.
Coronary Stents
What are they?
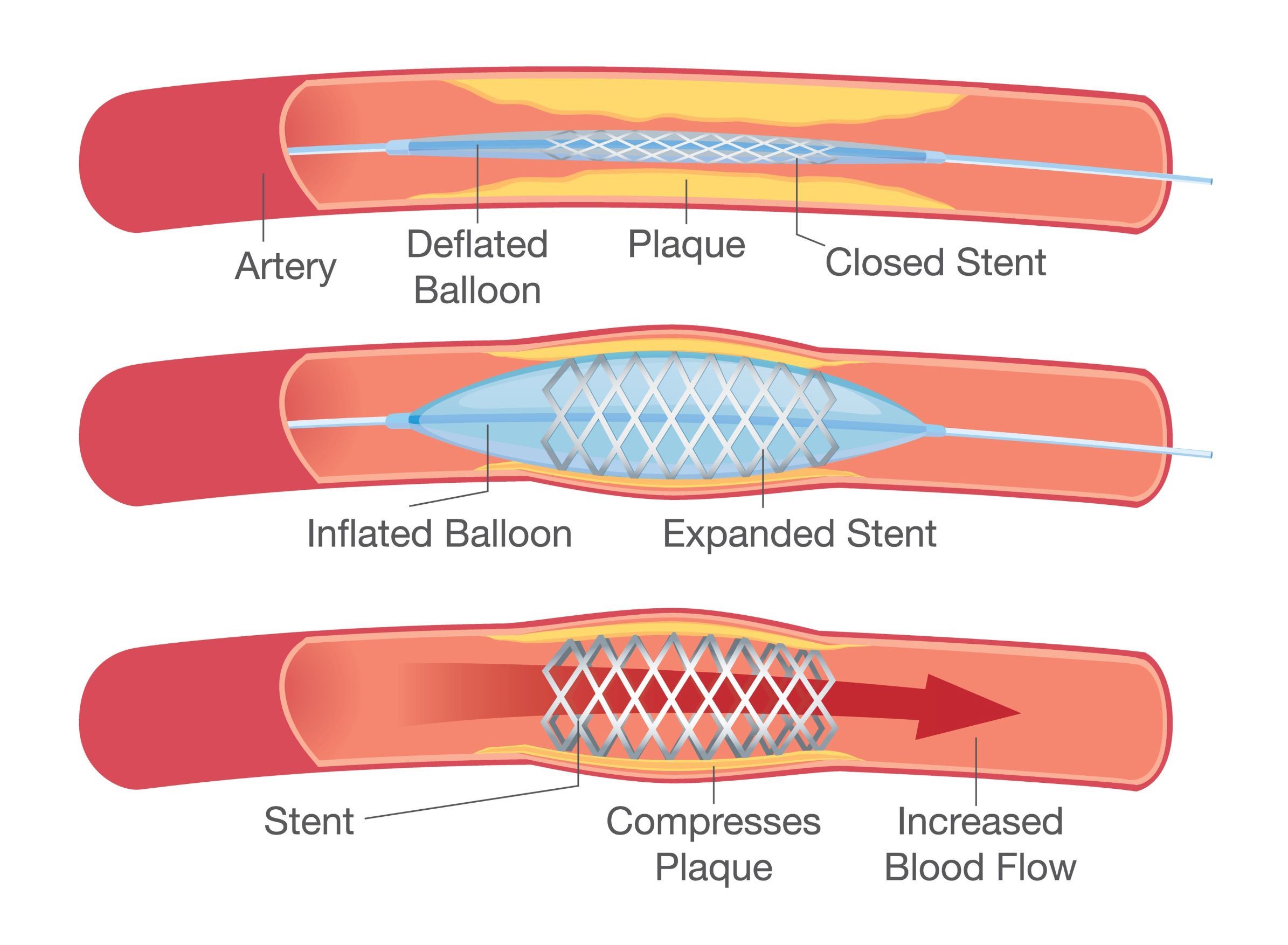
A stent is a tiny wire mesh scaffold that helps keep the artery open to maintain blood flow into the heart. In many cases, a stent is placed during an angioplasty. The doctor inserts a balloon catheter covered with the unexpanded stent into the blocked area of the artery. The balloon inflates, compressing the plaque against the artery wall and expanding the stent into place. Once the stent is fully expanded into the artery wall, the balloon is then deflated and removed.
Specialized Devices
Laser Atherectomy
A laser atherectomy is a specialized device that is used for eliminating plaque from arteries. During the procedure, the device is advanced over the wire through the artery until it reaches the blockage. This catheter has a laser at the tip, that emits high-energy light vaporizing the blockage, increasing blood flow through the artery. At this time, the doctor will determine if stents and /or balloons are needed to further treat the blockage.
Rotational Atherectomy
A rotational atherectomy is a specialized device that is used for eliminating plaque from arteries. During the procedure, the device is advanced over the wire through the artery until it reaches the blockage. This catheter has a high-speed revolving burr (oval shaped metal ball) at the tip which breaks up the plaque that is blocking blood flow, into tiny pieces that can pass through the artery. At this time, the doctor will determine if stents and /or balloons are needed to further treat the blockage.
Shockwave Lithotripsy
Shockwave Lithotripsy is a type of coronary angioplasty that uses shockwave technology to eliminate calcified blockages in the arteries. Plaque in the arteries may have evolved into hard calcium deposits, making it difficult to install a stent to keep the artery open. In this procedure, the doctor inserts a catheter covered with a balloon into the blocked area of the artery. Shockwaves from the catheter then transmit ultrasonic pressure waves that gently break down calcium deposits and soften the plaque. This allows the balloon to gently inflate and open up the artery. A stent attached to the catheter is then expanded into place, and the balloon is removed.


